MNEXT (Avans University of Applied Sciences) collaborates within ImPHAct! with Paques Biomaterials, Looop, and Cargill. A great partnership where MNEXT is responsible for project management, execution of laboratory work, data analysis, and communication.
PHA production
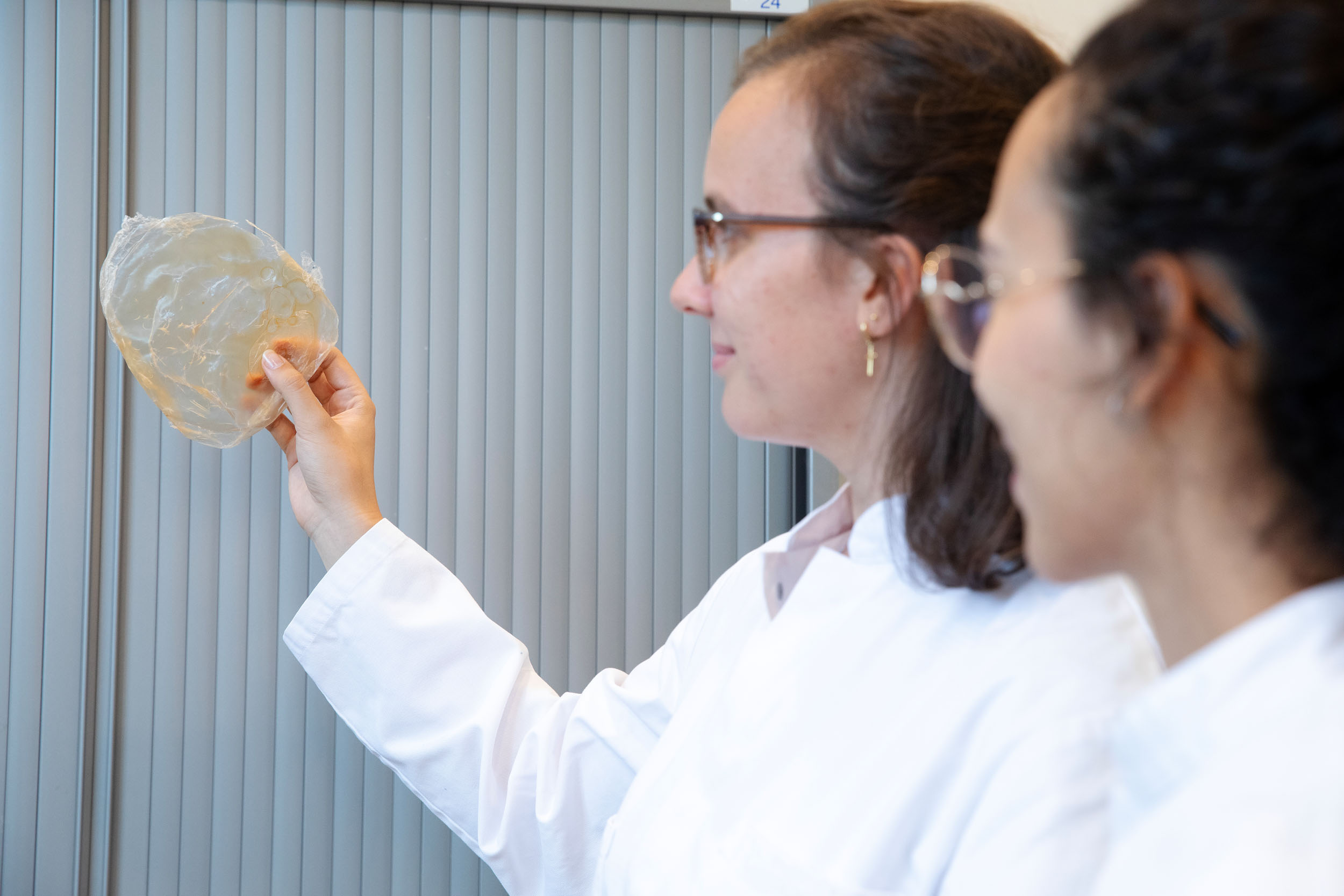
Now you might wonder: How do they make PHA from residual streams? Project leader Mithyzi Andrade Leal explains: “Bacteria use organic substances such as sugars and starches found in wastewater to make PHA. They do this by first converting the organic substances into so-called volatile fatty acids (VFAs). These VFAs can then be converted into PHA. This PHA is stored by the bacteria in their cells as a reserve energy source. If the bacteria are full of PHA, we remove the PHA from the bacteria,” says Mithyzi.
It is important to understand how different composition residual streams and fermentation parameters influence VFA production.
Volatile Fatty Acids
Even though there is already a lot of knowledge about the production of PHA, there are still steps that can be improved. One of these steps is converting the organic substances in the wastewater into VFAs such as acetic acid and propionic acid. “We want to be able to predict this process better so that we know better which VFAs are produced. This in turn ensures a more predictable and stable production of PHA,” says Mithyzi. How do they approach that? “We want to develop an innovative predictive model for the production of VFAs that integrates biological and chemical data. We do this by looking at the various factors that are important in the production of VFAs such as pH, temperature and time. We use the collected data to create a predictive model. We also use the data we have collected in previous projects”.
January 2024 until June 2025